- Review
- Open access
- Published:
Research progress and knowledge system of world heritage tourism: a bibliometric analysis
Heritage Science volume 10, Article number: 42 (2022)
Abstract
In the context of integrating culture and tourism, world heritage tourism research has become a focus in tourism research in recent years. There are increasing discussions in academic circles on the content and methods of this field. Clarifying the knowledge system of research is conducive to dialogue with international theoretical frontiers and integrating, analyzing, and predicting the progress and lineage from a more comprehensive perspective. Still, few studies on the knowledge system of world heritage tourism research have been conducted. To fill this gap, this study uses the SSCI and SCI sub-databases of Web of Science Core Collection as the data source with the help of CiteSpace and VOSviewer software to measure the knowledge system of world heritage tourism research. A bibliometric analysis of 567 publications between 1992 and 2020 was conducted to construct a framework of a knowledge system based on literature statistics and content analysis, revealing the geographic research regions, theories and methods, themes and contents, trend evolution, and future research inspiration. The results show that: (1) the number of publications tends to increase gradually, with the highest in 2019. The authors and research institutions are mainly concentrated in Europe, America, East Asia. China has the highest publications. More literature on cultural heritage as a geographical study area than natural heritage. (2) The research themes, objects, and methods of the sample literature have become more diversified with the advancement of the research stage. The literature on multi-stakeholder research is the largest, followed by tourism impacts and research on World Heritage Sites’ resource management techniques and methods. These studies provide a multifaceted interpretation of the sustainable development of World heritage tourism, mainly from the perspectives of both supply and demand. However, the theoretical system is still incomplete. (3) Future research should strengthen the theoretical system construction, research innovation, cooperation, and research exchange in world heritage tourism research. Pay more attention to the research on the pluralistic value system of world heritage. Focus on exploring research on world heritage tourism’s resilience and localization dilemmas under the impact of the New Crown epidemic. To reveal the synergistic mechanisms and paths of diversified livelihoods of World Heritage Sites’ residents in ecologically fragile and impoverished areas.
Introduction
Research on world heritage (WH) tourism began to emerge in the mid-twentieth century and has shown rapid growth in the early twenty-first century and continues today. A World Heritage Site (WHS) is a scarce area of outstanding universal value (OUV) that requires long-term protection, is non-renewable and irreplaceable, as identified by United Nations Educational, Scientific and Cultural Organisation (UNESCO) and World Heritage Committee (WHC) [1]. World Heritage-listed areas typically receive an order of magnitude more tourist visits than their non-listed counterparts [2,3,4]. These areas are also often used as a means of economic regeneration through tourism development [5,6,7], as they have a significant economic impact on local communities [8,9,10,11]. In addition, WHSs contribute to national image building [12,13,14] and promote destination branding [13, 15, 16]. Thus various national and regional governments actively apply for WHSs [15]. As of December 2021, the total number of enlisted heritage sites is 1154, including cultural, natural, and mixed categories, registered in 167 countries. In recent decades, WHSs have attracted a great deal of attention in promoting tourism and economic development and heritage conservation, driven by the benefits of the “WH” brand. The series of impacts and challenges arising from the inscription and development frenzy has led to a lively debate and a re-examination of WH tourism in the light of the increasingly popular concept of sustainable tourism development.
Tourism utilization and WH conservation are inevitably intertwined, and there is a symbiotic or tension between the two [17,18,19]. The development of tourism can create new values and social relations for WHSs and is often seen as a tool to combat poverty and promote sustainable development [8, 20,21,22,23]. However, many WHSs also face challenges by the rapidly expanding tourism industry, population pressure, environmental pollution, conflicts between residents, tourists, government, and other stakeholders threaten WH conservation and sustainability. The interaction between conservation and use has become a vital issue in WH tourism research [24,25,26,27]. Development pressure due to local socio-economic issues, poor legislation and management, and inappropriate tourism operations are the leading causes of conflicts between heritage conservation and tourism development [28,29,30,31].
Controversies in academic circles regarding WH tourism research are becoming increasingly intense, and differences in positions and perspectives have divided the study into different categories. For example, environmentalists believe that WH and tourism are entirely contradictory. The development of tourism poses a threat to the environmental protection of WHSs [31,32,33]. Scholars concerned with social development emphasize that tourism can promote the economic development of WHSs [5, 8, 22]. Socio-ecological conservation advocates focus on exploring the synergy between environmental conservation and tourism economic development in WHSs [34, 35]. It is essential to clarify WH tourism research’s progress and academic dynamics to advance research in the field, thus explaining the unique research objects and focus.
Existing studies have been categorized and reviewed mainly in terms of fundamental issues of WH tourism destinations, tourism activities, tourists, and other stakeholders, mostly an analysis of the content of the literature. While review studies based on bibliometric analysis have emerged in recent years, integrated accounting and prognosis of the development lineage of WH tourism research are relatively rare. A knowledge system is structured knowledge that members of a discipline or field use to guide their practice or work [36], including a systematization of the structure, principles, and examples of professional knowledge generated by members through continuous discovery and validation. The organization of the knowledge system facilitates the self-reflective growth and reproduction of WH tourism research [37]. A single visual knowledge map can hardly reflect the intrinsic nature of the knowledge system, and a single content analysis method is slightly lacking in objectivity. To fill this gap, this study mainly uses two types of scientometric tools, CiteSpace and VOSviewer, which integrates quantitative analysis represented by scientometric analysis, knowledge mapping, and keyword clustering, and content analysis represented by topic reading to identify the research progress and knowledge system of WH tourism research. To provide a comprehensive and objective overview of the current state of research in the field and provide a scientific reference for subsequent research. To achieve this, we set the following objectives:
-
To reveal the basic characteristics of the literature (section 3: changes in the number of publications, authors, research institutions, geographical research areas).
-
To identify key areas of research progress (sections 4–5: key research areas and contents, research theories and methods, and evolution of research trends).
-
To build a framework of knowledge (sections 6–7).
Material and methods
Research methods
Bibliometric analysis helps decipher and map the cumulative scientific knowledge and evolutionary nuances of well-established fields by making sense of large volumes of unstructured data in rigorous ways. It enables and empowers scholars to gain a one-stop overview, identify knowledge gaps, derive novel ideas for investigation, and position their intended contributions to the field [38]. In recent years, bibliometric analysis in heritage tourism has emerged sporadically [39, 40]. However, there is a relative lack of bibliometrics on tourism research in WHSs.
Science mapping is a generic domain analysis and visualization [41]. It is a study of scientific knowledge and belongs to scientometrics [42]. Several valuable scientific knowledge mapping tools have been born in bibliometric analysis, such as CiteSpace, VOSviewer, Sci2, BibExcel, Carrot2, etc. CiteSpace software can more intuitively and quickly visualize the focus and evolutionary trends in a specific field than other visualization and analysis software. It can reveal the inner connection between knowledge bases, conducive to better grasping the key points and future research development direction. VOSviewer software has unique advantages in graph display and clustering technology and is often used to display large networks [43]. The combined use of CiteSpace and VOSviewer software visualizes the highlights and trend evolution of WH tourism research. Using bibliometric visualization software for statistical data analysis, combined with content analysis, we objectively interpret WH tourism research progress and construct a knowledge system framework to provide scientific reference for WH conservation and utilization.
Material
Defining terms
WHS is a rare and irreplaceable treasure of humanity recognized by UNESCO and WHC as a heritage site and natural landscape of OUV. OUV is the criterion for being selected as a WHS. It means cultural and/or natural significance, which is exceptional to transcend national boundaries and be of common importance for present and future generations of all humanity. The World Heritage List (WHL) published by UNESCO divides WHS into three main categories: cultural site (including cultural landscapes), natural site, and mixed cultural and natural site. According to the Convention Concerning the Protection of the World Cultural and Natural Heritage (Convention) promulgated in 1972, world cultural heritage means cultural objects, architectural ensembles, and sites of OUV. World natural heritage refers to natural features of OUV, threatened animal and plant habitat areas, wild places of interest, or delineated natural areas. Only properties that partially or fully satisfy cultural and natural heritage definitions in Articles 1 and 2 of the Convention can be considered “mixed cultural and natural heritage.” Following the Convention’s definition of WH, we focus on the tourism development of world cultural, natural, and mixed heritage sites. Therefore, publications that meet the following conditions are excluded.
-
A study of heritage tourism unrelated to WHS.
-
Articles and comments on intangible heritage.
Document selection
In this study, we used the Web of Science (WoS) Core Collection database as the data source, selected one of the Science Citation Index Expanded (SCI) and Social Sciences Citation Index (SSCI) databases to search. The reason for using this database is that it is one of the most widely recognized international databases with data going back to 1900 and provides a rich, comprehensive collection of information from more than 18,000 authoritative, high-impact scholarly journals worldwide. Search the literature using 5 sets of keywords. (a) “world heritage” and “tourism,” (b) “world cultural heritage” and “tourism,” (c) “world natural heritage” and “tourism,” (d) “mixed heritage” and “tourism,” (e) “cultural landscape,” “world heritage” and “tourism.” Without limiting the starting time, the data were last updated on December 31, 2020.
Searches returned 672 documents (Fig. 1): (a) 604 documents for world heritage and tourism, (b) 29 documents for world cultural heritage and tourism, (c) 24 documents for world natural heritage and tourism, (d) 3 documents for mixed heritage and tourism, and (e) 12 documents for cultural landscape, world heritage and tourism. We excluded 10 documents not in English, and 28 documents that appeared in two searches or more (duplicates). Finally, a full-text assessment was carried out, resulting in 567 papers (Additional file 1: Appendix S1).
Document analysis
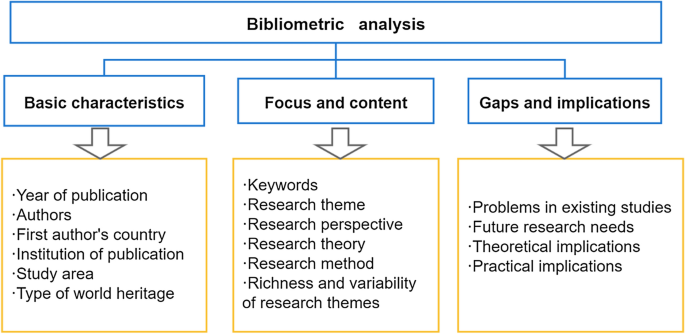
In the final data analysis phase, an analysis protocol has been applied to critically analyze the collected publications’ content and describe it in a structured way (Fig. 2). It sought to gather each document’s essential characteristics, focus, content, and existing gaps and needs in WH tourism research. Finally, a full-text assessment was conducted to summarize findings and problems with existing studies and present future research needs.
Basic characteristics of the selected publications
Year of publication
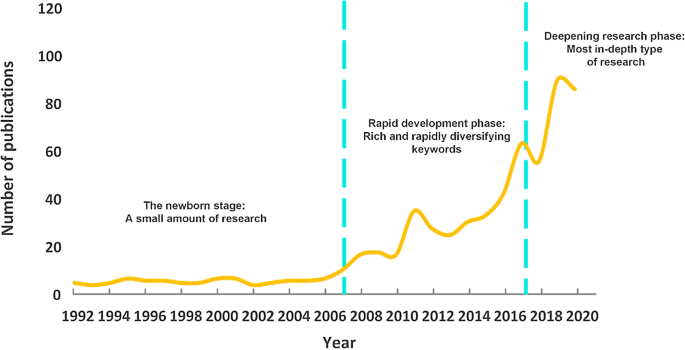
As shown in Fig. 3, the number of publications generally showed an upward trend from 1992 to 2020. At the end of the twentieth century, related scholars began to pay attention to this emerging field, and the results appeared one after another. However, the number of articles published between 1992 and 2006 was small because of the initial research stage, with an average of only 2 articles per year. Since 2007, the number of articles has increased significantly, in 2019 was as high as 94, indicating that the academic community’s research on world heritage tourism is highly enthusiastic.
First author’s country
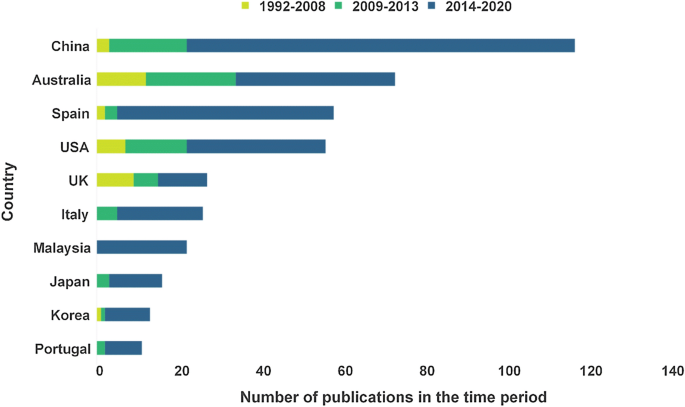
The sample literature came from more than 50 countries in total, and the top 10 countries in terms of the number of publications were mainly concentrated in East Asia, Europe, and America (Fig. 4). China has the most significant number of publications, accounting for 20%. The early research literature was mainly concentrated in developed countries like Australia and the United Kingdom. Research in China began to appear in 2003, with a significant increase in volume in 2009, and maintained the world’s top-ranking number of publications during 2014–2020. Since China joined the Convention in 1985, it has become one of the fastest-growing countries in the world in terms of the number of WHSs, attracting the attention of the academic community and increasing the number of research results year by year. By the 43rd World Heritage Conference, 55 WHSs have been successfully nominated, ranking first in the world with Italy. It can be seen that the geographical distribution of research literature is positively related to the level of regional economic development and the number of WHSs.
Authors and institutions
(1) Authorship and cooperation networks
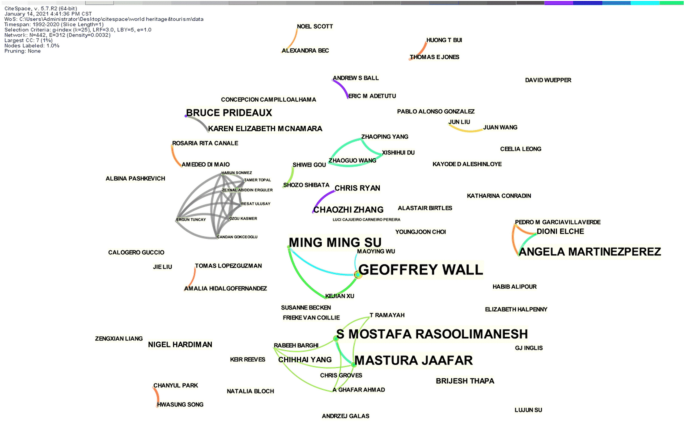
There were 475 first authors on the 567 sample papers. In Fig. 5, the larger font size of the authors’ names indicates more publications, and the larger nodes indicate more collaboration between authors. It shows that Su, Rasoolimanesh, Martinez-Perez A, Xu, and Buckley are the top five in terms of the total number of publications. And the collaborative network has a core–edge structure with fewer connections between the nodes, indicating that only a few researchers collaborate, and the majority of scholars are weakly connected. Most research teams were formed after 2011, indicating that research on WH tourism has gradually increased since then. For example, Su and Wall have collaborated on many publications on community engagement in heritage sustainable management research. Rasoolimanesh and Jaafar have produced many results around resident perception research in heritage sites, with 6 articles published in 2016.
(2) Issuing institution
According to the frequency in Table 1, the top ten research institutions in terms of the number of publications are mainly universities and colleges, and there are relatively few research institutes. Sun Yat-Sen University and the Renmin University of China are the primary research institutions in China. The rest of the research institutions are mainly located in Canada, Australia, Spain, and Malaysia. Research institutions have specialized WH tourism research groups, such as Sun Yat-sen University in China, whose primary literature is contributed by the team of Zhang, Xu, and Sun.
Geographical study area
There are 56 world natural heritage sites and 123 cultural heritage sites studied in 434 documents. 155 of these articles (36%) are about natural sites, 254 (59%) about cultural sites, and 25 about mixed heritage sites (5%). The WHSs that appeared more than 2 times in the sample literature were counted and sorted by their countries (Table 2). It shows that China, Australia, Spain, Malaysia, Korea, and Cambodia are the hot geographical areas of academic research, with the Great Barrier Reef (n = 18), Melaka and George Town (n = 15), and Angkor (n = 11) being the most prominent. In recent years, research results about Jiuzhaigou Valley Scenic and Historic Interest Area and Wulingyuan Scenic and Historic Interest Area in China and the archaeological heritage of the Lenggong Valley in Malaysia have increased.
Key research areas and content
Keywords
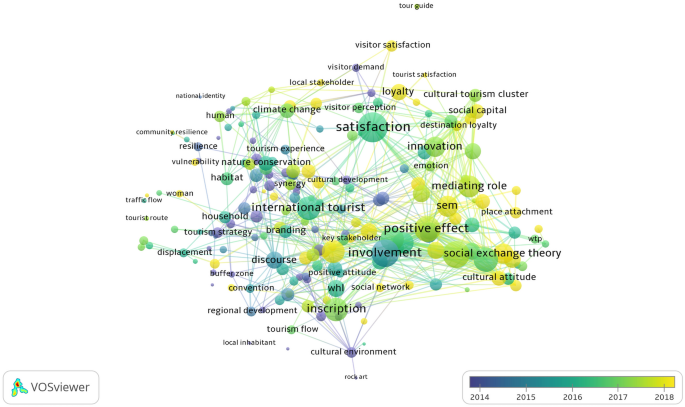
Keywords are a condensation and distillation of the core content of the literature. A high frequency of keywords can reflect the focus in a particular area [44]. Using the CiteSpace keyword analysis function to identify the main topics of interest to the academic community. Table 3 shows the keywords with a word frequency greater than 10 times. It can be seen that management, conservation, impact, perception, satisfaction, sustainable tourism, and stakeholders are the concerns in WH tourism research. In addition, we found that keywords such as customized authenticity, adaptive management, social-ecological system, sustainable livelihood, and resilience had a word frequency of fewer than 5 times, giving us some clues to track the frontier. Although the high-frequency keywords can reflect the main focus of existing research, the article’s overall idea and the mainline cannot be seen through the keywords.
Research themes
After identifying the high-frequency keywords, the research themes in the field were further clarified. To avoid the limitation of keywords, combining keyword clustering with full-text reading, the key research areas of WH tourism research were summarized into the following 8 themes.
(1) Sustainable tourism
The sustainable tourism theme contains 86 articles (15% of total). Scientific research has always been very focused on assessing the sustainability of tourism [45]. The development of governmental sustainable management strategies (n = 25), community residents’ perceptions and attitudes towards participation in tourism development (n = 28), spatial evolution of destinations (n = 8), low-carbon environmental measures in ecotourism (n = 12), and community livelihood diversification (n = 13) have been studied as factors influencing sustainable tourism in WHSs. Among them, the most crucial academic attention has been paid to the relationship between community support and sustainable tourism. Several empirical studies have been conducted, showing that local and community participation in WH management is necessary for sustainable tourism [46, 47]. Empowering local communities to participate effectively in tourism decision-making and to be able to share equitably in the benefits of tourism development is an essential principle of sustainable tourism [25, 48,49,50,51,52]. Sustainable tourism has been widely accepted to mediate tensions and balance the relationship between heritage conservation, tourism management, social pressure, and economic development.
(2) Authenticity
The theme includes 14 articles (2% of total). The UNESCO have adopted authenticity as a critical principle for inscription on the WHL [1]. In the tourism context, three commonly used authenticity concepts are objective authenticity, constructive authenticity, and existential authenticity [53]. Studies of authenticity in WH tourism focus on existential authenticity (n = 10) and constructive authenticity (n = 4). Existential authenticity emphasizes tourists’ perceptions, experiences, and preferences of authenticity, including experiences, emotions, attachments, and identities [54]. Scholars generally agree that the authenticity of the tourist experience has a significant impact on satisfaction and loyalty and that the quality of WH tourism is enhanced by authenticity [55,56,57,58,59]. The perception of authenticity increases the heritage destination value [60]. Constructed authenticity discussions focus on customized authenticity that tourists can seek and embrace even in publicly staged or produced contexts [61]. The debate on the authenticity of WH tourism has shifted from the static perspective to how authenticity is interpreted [62]. The acceptance of authenticity itself depends on tourists’ perceptions.
Authenticity is a controversial concept in WH tourism studies [53, 63]. Some scholars have even suggested that the concept should be abandoned because of its problematic nature [64]. Despite its clear importance, authenticity is a problematic and insufficiently explored concept, which hinders its practical application [53]. So fewer articles are examining the use of authenticity in WH tourism practice. However, with the rapid development of WH tourism and the microscopic shift in WH tourism research, Scholars have attempted to explore the impact of different authenticity on the visitor experience. They have confirmed that understanding how visitors interpret authenticity is vital for marketing and managing heritage sites [56, 57]. After 2017, there has been a marked increase in research on the application of authenticity in WH tourism practice. The number of articles is relatively small because it is still exploratory.
(3) Management techniques and methods of tourism resources
The second-highest number of publications (22% of the total) studied management techniques and strategies for WH tourism resources, with 124 articles. Dynamic conservation and multidisciplinary research are fundamental approaches to planning and sustainable management of WH. The main focus is on techniques and methods for WH resource survey and assessment (n = 32), management and conservation enhancement (n = 57), presentation and education (n = 14), visitor flow forecasting (n = 3), visitor safety management (n = 6), and itinerary design (n = 12). Thanks to the continuous progress of technology, a series of new technologies and methods such as 3D technology [65], geoinformation technology, and remote sensing(RS) [66, 67], augmented reality(AR) [68], and mixed reality (MR) [69] have facilitated the management and conservation of WH tourism resources. Western scholars focus on the physical conservation of heritage sites, and research and conservation also focus on achieving this goal through technology [65, 70, 71]. Recently, scholars have taken social-ecological system theory [34], adaptive management theory [72], and resilience theory [35, 73] to analyze the resource conservation and tourism development contradictions and propose synergistic paths on this basis.
(4) Tourism impacts
There are 110 articles on the tourism impacts (20% of total). The impacts of tourism on WHSs is mainly environmental (n = 50), economic (n = 13), social (n = 15), and cultural (n = 5), with some studies discussing the combined impact (n = 27). There is a consensus in the academic community that demographic pressure from tourism remains a major threat to WHSs’ environmental and cultural integrity. Highly intensive tourist demand significantly challenges the sustainability of WHSs [74, 75]. In addition, local socio-economic development pressures and mismanagement also pose challenges to its health. Most studies have examined the objective environmental impacts by assessing tourism environmental capacity, ecological tourism footprint, and eco-efficiency. The destruction of the natural environment and ecosystems of WHSs and the intensification of environmental pollution of air, water, vegetation, soil, etc. are the major negative environmental impacts [31,32,33, 76,77,78,79], or assessing the environmental impacts from the perspective of residents’ perceptions [10, 80, 81]. Tourism development contributes to sustainable livelihoods, women’s empowerment and gender equality, and improved recreational facilities and public amenities in WHSs [9, 22, 23, 82,83,84]. However, it can also result in negative impacts such as increased cost of living, rising real estate and prices, income imbalance, littering, and host-client conflict [85]. In addition, scholars represented by Jimura, Rasoolimanesh, and Kim have confirmed through their studies that the rapid development of WH tourism has improved the cultural identity of residents to some extent. Traditional arts and culture have been preserved and revived to some extent. Still, it has also weakened the local spirit of local communities and created a series of conflicts between village historical heritage conservation and tourism development [8, 9, 80, 86, 87].
(5) Stakeholders
This topic has the largest publications, including 143 articles (25% of total). WH tourism stakeholders were studied mainly by residents (n = 45), tourists (n = 54), government departments (n = 19), tourism enterprises (n = 10), and multiple stakeholder interactions (n = 15). Scholars often use perception studies as a breakthrough to study stakeholder synergy. Visitor perception studies are useful for understanding their motivations and expectations for undertaking WH tourism, strengthening visitor management, and promoting destination marketing and promotion. Studies have been conducted on visitor perceptions mainly from heritage presentation and interpretation, marketing, and management. The research mainly focuses on the relationship between tourists’ perceived value, quality of experience, satisfaction, and loyalty [88,89,90,91,92,93,94]. The perceived impact of tourism development by community residents is a key and necessary element of community engagement research [25, 95,96,97]. Scholars have studied residents’ perceptions or attitudes through cross-sectional and longitudinal comparisons. They agree that socio-economic status, local attachment, environmental attitudes and values, and participation in the planning and decision-making process become the main factors determining residents’ perceptions of tourism impacts [98, 99]. The local attachment is the most critical element [100].
As the leading force in the “inscription” process, the government is the guarantor of the rational development of heritage tourism resources and the involvement of stakeholders. Many issues hinder the sustainable development and management of heritage tourism in developing countries. Lack of political will, government priorities, and financial assistance are the main constraints to WH management [101,102,103]. Although governments do not hesitate to develop tourism, their mismanagement is inevitably criticized [104,105,106]. Travel agencies and tourism companies are an integral part of WH conservation. Research on tourism companies has focused on maximizing economic benefits and exploring breakthrough innovations at the firm level in the context of cultural tourism clusters [107, 108]. The perceptions of corporate managers regarding their social responsibility in WH conservation have not received much attention from scholars [109, 110].
(6) World heritage value
21 papers discuss the value of WH (4% of total). The study is mainly focused on OUV (n = 8), economic value (n = 6), and social value (n = 7). Research on OUV of WH focuses on different stakeholders’ perceptions of heritage values and the factors that influence them. Some studies focus on discussing OUV narration from a guide’s perspective [111, 112]. However, the understanding and claiming of the pluralistic value of heritage has not been given much attention. Tourists’ tourism satisfaction and education level are the main factors influencing their perception of OUV [113, 114]. Residents’ perception of OUV positively impacts local attachment and willingness to preserve heritage. The conditional value assessment method (CVM) is a commonly used method for estimating the economic value of WHSs, providing a scientific reference for admission management systems and better brand marketing [86, 103, 115, 116]. In addition, recent studies have explored how to construct heritage social values based on OUV and have indicated that social values are beneficial to enhance the international and national image and tourism attractiveness of WH destinations [117]. Heritage values are artificially assigned by different heritage subjects rather than naturally generated and self-evidently existing. The identified OUV emphasizes the materiality of heritage with a Eurocentric perspective. However, there is also a need to focus on non-material content such as people and activities associated with WHSs to better convey heritage stories and a sense of place [112, 118].
(7) Destination brand image building and marketing
The theme includes 40 articles (7% of total). Studies have focused on WH brand equity management (n = 11), marketing strategies, platforms and tools (n = 12), stakeholder perceptions of WHS brand image (n = 8), visitor market segmentation (n = 5), and heritage promotional discourse (n = 4). WH represents the international identity of the inducted country, and it can play an essential role in building a national image and the highly competitive global tourism market [12]. The success of the inscription is a great honor for the selected country, and the “WH” brand is widely used in marketing campaigns to promote national tourism and increase the destination’s visibility. Scholars generally agree that the WHL helps build destination images [13, 119] and discusses using the WH brand for destination image building and marketing. It is also argued that establishing emotional attachment to build destinations and the interpretation of authenticity by tourists are vital issues in branding tourism destinations in today’s tourism market [56, 120]. Although the WHL is a powerful brand that significantly impacts tourism, it still requires proper management to maintain brand equity. However, brand image building and marketing need to be integrated with the local culture [121], focus on local storytelling, and highlight the elements that characterize its heritage value to develop differentiated marketing.
(8) Impact of the World Heritage List on tourism demand
The literature examining the impact of the WHL on tourism demand includes 29 articles (5% of total). The majority of scholars see “inscriptions” and “accessions” as “magnets” that attract tourists and guarantee an increase in the number of visitors to heritage sites. They generally believe that “inscription” positively impacts local tourism demand (n = 22). It has been shown to have a positive impact on local tourism demand through the use of “inscription” in China [4, 122,123,124], Italy [125, 126], Spain [127], Israel [15], and other case studies confirm this finding. Contrary findings (n = 7) argue that the WHL does not necessarily promote tourism [128,129,130]. Some scholars in the recent literature have questioned the assumption of a linear relationship between the total number of WHSs and tourism demand in previous studies, emphasizing the need to distinguish between the different impacts of tangible and intangible heritage on tourism demand [131]. The effects of the WHL on heritage tourism vary from country to country and region to region, with findings running depending on the study area, research perspective, and methodology. The disagreement among scholars makes the research on the effect of WHL on tourism demand consistently popular [4, 130, 132].
Research theory and methodology
Given the small number of high-frequency keywords regarding research methods reflected in Table 3, all keywords were analyzed in this paper to gain insight into the main theories and methods in the field. In addition, a glossary of terms representing specific research theories and methods was summarized by analyzing the content of the literature (Table 4). Various well-established theories such as sustainability development theory (n = 67), community participation theory (n = 62), stakeholder theory (n = 25), place attachment theory (n = 17), authenticity theory (n = 16), sustainable livelihood (n = 13), social-ecological system theory (n = 10), resilience theory (n = 7), social exchange theory (n = 6), and planned behavior theory (n = 5). Scholars have used these theories to argue for problem and pathway studies of WH tourism. Research methods are mainly qualitative (n = 151) and quantitative (n = 327), or a combination of both (n = 89), and quantitative analysis methods are becoming increasingly diverse.
Evolution of research trends
With the continuous advancement of WH conservation practices, WH tourism research themes are becoming increasingly diverse (Fig. 6). Based on the number of publications, keyword clustering analysis, and interpretation of the leading research content of the literature, the following stages are used to characterize the evolution of research trends in this field.
The first stage (1992–2006): the newborn stage. The number of WHSs grew slowly during this period, and research in WH tourism is beginning to receive attention, but not much heat. The literature in this stage is small, and the clustering of keywords is not apparent because of the small amount of literature. The research package mainly includes the functional zoning planning of WHSs, the impact of tourism activities on the natural environment, and the impact of national tourism policies on the development of WHSs. More studies at the macro level mainly focus on proper conservation management of tourism resources and exploring sustainable development strategies. In addition, there are more studies on the management and conservation of WH based on tourists’ perspectives, emphasizing the management of tourists to promote the WH conservation. In terms of resource types, there are more case studies about the Great Barrier Reef, a world natural heritage site.
Phase 2 (2007–2017): rapid development phase. During this period, the proliferation of WHSs and the range of challenges and impacts of tourism overdevelopment have generated a lively debate in academic circles. The publications showed a rapid growth trend in 2007 and beyond, with increasingly rich keywords and rapidly diversifying research themes. Theoretical thinking and practical research have been expanded, and research perspectives have been broadened with distinctive interdisciplinary features. The research on WH conservation gradually changes from “balancing conservation and development” to the paradigm of “conservation for development.” Therefore, besides focusing on the conservation of heritage resources, the socio-economic benefits of WH are gradually being paid attention to, and the impact of WHL on tourism demand has become a more intense issue of debate among scholars. In addition, the conservation philosophy of world natural heritage sites is undergoing a shift from neglecting communities to valuing them, from absolute conservation to gradient conservation, and paying more attention to human needs and development. Therefore, studies on multiple stakeholders have become more prosperous. Residents’ perception, community involvement, local attachment, tourists’ experience, tourists’ loyalty, and satisfaction and the relationship between them have become the focus of scholars’ attention.
Phase 3 (2018-): deepening research phase. The WH has moved from rapid quantitative growth to enhanced conservation and management quality. Research in this period expands slowly and is the most in-depth type of research. New ideas such as digitalization, cultural creativity, and low-carbon tourism are also penetrated in WH resource conservation. Scholars began to focus on areas such as the evolution of cultural space in WHSs, the construction of WH brand assets, residents’ responsibility and attitude towards heritage conservation, well-being, and the resilience of socio-ecological systems. Meanwhile, further deepening research on the impact of the WHL on tourism continuity, the spatial and temporal evolution of residents’ perceptions, the promotion of destination images and brand effects, the construction of heritage authenticity, and sustainable livelihoods of communities. Continued attention is paid to exploring pathways for the management and sustainable tourism development of WHSs.
Knowledge system framework for world heritage tourism research
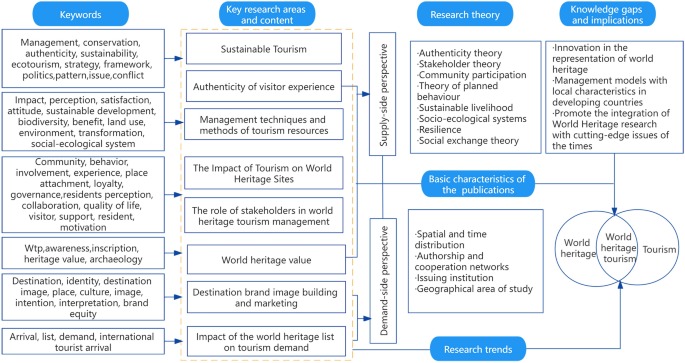
To better understand the progress and lineage of WH tourism research, a framework of knowledge system is constructed. This framework is based on the basic characteristics of the literature, the key research areas and content, research theories, the evolution of research trends, and future research gaps summarized in the previous section [133] (Fig. 7). The first box’s contents in the left column are derived from high-frequency keywords. The keywords in each box are sorted in word frequency from highest to lowest. For example, in the first box of the first column, the highest frequency is “management,” and the lowest is “conflict.” The sustainable tourism theme is summarized by extracting 11 keywords and interpreting the content of the literature and presented inside the first column of key research areas and content. The other 7 themes were extracted by the same method. The endpoint of the whole knowledge system framework points to two intersecting circles. It consists of three high-frequency keywords: “world heritage,” “tourism,” and “world heritage tourism,” indicating that world heritage and tourism are inseparable.
Around the binary debate of conservation and utilization, the conservation and management practices and the tourism and leisure practices of WHSs have become two main lines of research, respectively. Research perspectives are mainly cut from both supply and demand sides but are not discrete. For example, WH tourism authenticity focuses on both the interpretation of authenticity by tourists in the demand perspective and the management and development of heritage resources in the supply perspective. The supply-side perspective emphasizes the study of destination management, the tourism impacts on WHSs, and stakeholders such as communities and governments in management as the focus of WH tourism. In particular, the ecological, social, economic, and cultural impacts of tourism on WHSs, sustainable livelihoods, and community perceptions have received continued attention from scholars. The demand-side perspective focuses on WH tourism from a marketing perspective, with branding and marketing of destinations, the impact of the WHL on tourism demand, and the relationship between visitor experience, perception, and satisfaction as the primary research components.
In terms of research theories, academics mainly draw on relevant theories from sociology, anthropology, and ecology to explain and solve the contradiction between WH conservation and tourism development. The interdisciplinary trend is more prominent. However, there is a lack of theoretical research on geography. From the perspective of the human-land relationship system in WHS, future research should fully use geography’s comprehensive and systematic nature. And apply it more to the management techniques and methods of WH tourism resources to better understand the contradiction between WH conservation and tourism development and balance the relationship between them.
Knowledge gaps with implications for future research
WH tourism research focuses on the conservation and use of WHSs and examines the development of society through the interaction of the two. How to realize the synergy between WH conservation and tourism development will be a continuing focus of scholars in this field of research. Future research can focus on exploring the following areas.
Innovative ways of representing World Heritage
From a demand-side perspective, subsequent WH tourism demand research should focus on people’s subjective constructs, such as tourists’ cultural needs and preferences. To match consumer perceptions with the intrinsic values characterized by WH [14] and target brand building and marketing. Demand research on the supply side should explore how to cut through the origin and form of WH and bring heritage back to today’s social life through the industrialization of cultural tourism. The storytelling of WH and cultural communication in WH tourism should be the focus of scholars’ later research. Among them, local culture plays a vital role in the sustainable management of WHSs, and intangible elements such as memories, emotions, and feelings related to WHSs should also attract the attention of scholars. In addition, most of the current studies are on cultural heritage, while there is relatively little research literature on the cultural lineage of natural heritage. Future research should strengthen the value of natural heritage constructed based on OUV and pay attention to local spiritual maintenance and humanistic values. Mainly focus on exploring the mechanism of the construction of cultural confidence and cultural identity in WH conservation and exploring the synergistic path of heritage conservation and tourism development.
To explore world heritage management models with local characteristics in developing countries to synergize conservation and tourism development
Compared with leading foreign studies, WH tourism research in developing countries is more concerned with management systems, government policies, and community participation. Most of the existing studies have explored the issues themselves. There are more case studies and fewer studies that summarize the patterns. More attention needs to be paid to micro-area studies to draw on the results and paradigms of current research. Taking China as an example, localized management and development models should be explored in light of the unique characteristics of WHS, such as focusing on the sustainable development of WHS in karst ecologically fragile and poor areas. It is necessary to propose targeted WH tourism management policies based on adaptive and collaborative community management [77] and seek a win–win model for WH conservation and regional development. A multi-element, multi-scale and multi-system approach should be adopted to explore the evolutionary patterns of tourism development in WHSs. The aim is to strengthen the capacity to predict the evolution of WHSs’ spatial patterns and structures and improve the ability to regulate and support decision-making for sustainable development. In addition, it is necessary to build an inclusive, democratic, and dialogical space, deepen the research on the role mechanisms of different stakeholders in WH conservation and tourism development, pay attention to the research on the value perception and local attachment of tourism business managers, further clarify their social responsibilities, attitudes, and behaviors, and their influencing factors, and optimize their roles in heritage conservation and management. At the same time, it should strengthen the research on the localization dilemma of WH under the influence of the new corona epidemic and focus on the multiple livelihood synergy mechanism and path of residents in WHSs in ecologically fragile and poverty-stricken areas.
Promote the integration of World Heritage research with cutting-edge issues of the times
The help of modern science and technology such as big data, cloud computing, the internet of things, artificial intelligence, digital conservation technology, interactive display technology, information space management technology, and other vital technologies provide new paths for comprehensive, systematic, and complex research on WH. They provide scientific and technological support to expand further the depth and breadth of research on WH tourism. Subsequent research should focus on combining technology and local heritage characteristics, highlighting the “materialization” of technology while emphasizing humanistic care. In addition, the new crown epidemic has exposed and exacerbated tourism’s vulnerability, especially for communities that are highly dependent on tourism as a source of livelihood, and sustainability is threatened. At the same time, the epidemic has also had a tremendous impact on government management practices, tourist travel behavior, tourism business operation models, changes in management models, host-client relationships, market demand, and consumption habits. They are making it necessary to explore adaptive management models and future directions for the industry appropriate for local practices. Finally, resilience theory emphasizes studying the historical relationship between society and its environment. The study of the mechanism of community resilience on WH conservation may become a breakthrough point for adaptive management research. In the future, we need to pay attention to the study of the resilience path of WH tourism after the new crown epidemic to enhance the resilience of communities in WHSs.
Conclusion
Based on the “Web of Science” database, the knowledge mapping software CiteSpace and VOSviewer were applied, combined with bibliometric and content analysis methods, to reveal the knowledge system’s themes, trends, and frameworks of WH tourism research. From the essential characteristics of the literature, chronologically, the research began in the 1990s, achieved rapid development in the first decade of the twenty-first century, and is booming. It is mainly concentrated in countries and regions with rich WH resources, developed economies, and more mature tourism industries. Although a specific group of authors has been formed, a particular research circle has not yet been created. The cooperative relationship between most authors is weak. Research institutions are mainly concentrated in universities.
The increasing refinement of WH conservation concepts and tourism development practices has contributed to research trends. The evolution of the research phases shows that WH tourism research has gradually become more microscopic and specific, with further development of theoretical analysis and scientific practice and the expansion of the study to multiple stakeholders such as tourist objects and external societies. Research topics have shifted to the micro-level, such as residents’ perceptions of tourism impacts and the cultural and economic impacts on WHSs. As research deepened and diversified, several new concepts and techniques began to be applied to WH resource conservation and evaluation. Although the expansion of research has gradually slowed down, deepening research exploring the multidisciplinary intersection and multiple research methods and perspectives have further advanced.
The knowledge system has formed a multidisciplinary and multi-level comprehensive research situation. In terms of research methods, the combination of qualitative and quantitative is the main focus. The methods of quantitative analysis are becoming more and more diversified, mostly cutting from micro cases for empirical research, and the research content is mainly focused on both supply and demand of WH tourism. However, the theoretical system is not yet perfect. The knowledge mapping, constructed knowledge systems, and inherent knowledge linkages presented in WH tourism research have specific academic value. The evolution of the knowledge system further deepens the disciplinary innovativeness. Whether from supply or demand, future research should seek breakthrough points based on existing research, innovate WH representation, tell heritage stories, and strengthen research on the cultural lineage of natural heritage sites. To promote the integration of WH research with cutting-edge issues of the times, research the paths of resilience and localization dilemmas of WH tourism after the new crown epidemic, and focus on the inhabitants of WHSs in ecologically fragile and impoverished areas. We will also study the mechanism and paths of multi-livelihood synergy for residents in environmentally vulnerable and poor regions. We will strengthen theoretical system construction, research innovation, and exchange and cooperation to form a more prosperous and in-depth knowledge system of WH tourism research.
Availability of data and materials
Data sharing is not applicable to this manuscript as no datasets were generated or analyzed.
Abbreviations
- WH:
-
World Heritage
- WHS:
-
World Heritage Site
- UNESCO:
-
United Nations Educational, Scientific and Cultural Organisation
- WHC:
-
World Heritage Committee
- WHL:
-
World Heritage List
- Convention:
-
Convention Concerning the Protection of the World Cultural and Natural Heritage
- CVM:
-
Conditional value assessment method
- GIS:
-
Geographic information system
- PLS-SEM:
-
Partial least square-structural equation modelling
- AHP:
-
Analytic hierarchy process
- PCA:
-
Principal component analysis
- ANOVA:
-
Analysis of variance
- RS:
-
Remote sensing
- AR:
-
Augmented reality
- MR:
-
Mixed reality
References
UNESCO World Heritage Centre. Operational guidelines for the implementation of the world heritage convention. WHC.21/01. Paris: UNESCO, 2021. https://whc.unesco.org/en/guidelines/. Accessed 17 Jan 2022.
Yang CH, Lin HL, Han CC. Analysis of international tourist arrivals in China: the role of world heritage sites. Tour Manag. 2010;31(6):827–37.
Gao YY, Su W. Is the world heritage just a title for tourism? Ann Tour Res. 2019;78: 102748.
Han W, Cai JM, Wei YG, Zhang Y, Han Y. Impacts of the world heritage list inscription: a case study of Kaiping Diaolou and Villages in China. Int J Strateg Prop Manag. 2020;24(1):51–69.
Buckley R, Shekari F, Mohammadi Z, Azizi F, Ziaee M. World heritage tourism triggers urban–rural reverse migration and social change. J Travel Res. 2020;59(3):559–72.
Agapiou A. UNESCO World Heritage properties in changing and dynamic environments: change detection methods using optical and radar satellite data. Herit Sci. 2021;9(1):1–14.
Su MM, Wall G, Xu KJ. Heritage tourism and livelihood sustainability of a resettled rural community: mount Sanqingshan world heritage site, China. J Sustain Tour. 2016;24(5):735–57.
Jimura T. The impact of world heritage site designation on local communities—a case study of Ogimachi, Shirakawa-mura, Japan. Tour Manag. 2011;32(2):288–96.
Zhang X. Impact of rural tourism on residents’ well-being in traditional ancient villages: a case of North Guangxi. Herit Sci. 2021;9:138.
Slabbert E, Du Plessis E, Digun-Aweto O. Impacts of tourism in predicting residents’ opinions and interest in tourism activities. J Tour Cult Chang. 2021;19(6):819–37.
Christensen J, Jones R. World heritage and local change: conflict, transformation and scale at Shark Bay, Western Australia. J Rural Stud. 2020;74:235–43.
Silverman H. Border wars: the ongoing temple dispute between Thailand and Cambodia and UNESCO’s world heritage list. Int J Herit Stud. 2011;17(1):1–21.
Kim H, Stepchenkova S, Yilmaz S. Destination extension: a faster route to fame for the emerging destination brands? J Travel Res. 2019;58(3):440–58.
Wang ZG, Yuan BC. Harmonizing the branding strategy of world natural heritage in China: visitors’ awareness of the multiple brands of Wulingyuan, Zhangjiajie. Geoheritage. 2020;12:1–11.
Poria Y, Reichel A, Cohen R. World heritage site—is it an effective brand name? A case study of a religious heritage site. J Travel Res. 2011;50(5):482–95.
Xu HG, Ye T. Dynamic destination image formation and change under the effect of various agents: the case of Lijiang’, The Capital of Yanyu’. J Destin Mark Manag. 2018;7:131–9.
Li Y, Lau C, Su P. Heritage tourism stakeholder conflict: a case of a world heritage site in China. J Tour Cult Change. 2020;18(3):267–87.
Panzera E, De Graaff T, De Groot HL. European cultural heritage and tourism flows: the magnetic role of superstar world heritage sites. Pap Reg Sci. 2021;100(1):101–22.
Ryan C, Zhang CZ, Deng Z. The impacts of tourism at a UNESCO heritage site in China—a need for a meta-narrative? The case of the Kaiping Diaolou. J Sustain Tour. 2011;19(6):747–65.
Vargas A. The tourism and local development in world heritage context. The case of the Mayan site of Palenque, Mexico. Int J Herit Stud. 2018;24(9):984–97.
Lin YX, Chen MH, Lin BS, Su CH. Asymmetric effects of cultural and natural world heritage sites on tourism receipts. Curr Issue Tour. 2020;23(24):3134–47.
Su MM, Wall G, Xu KJ. Tourism-induced livelihood changes at Mount Sanqingshan world heritage site, China. Environ Manag. 2016;57(5):1024–40.
Maruyama NU, Woosnam KM. Representation of ‘mill girls’ at a UNESCO world heritage site in Gunma, Japan. J Sustain Tour. 2021;29(2–3):277–94.
Drost A. Developing sustainable tourism for world heritage sites. Ann Tour Res. 1996;23(2):479–84.
Rasoolimanesh SM, Jaafar M. Sustainable tourism development and residents’ perceptions in world heritage site destinations. Asia Pac J Tour Res. 2017;22(1):34–48.
Zhen RC, Chao YF, Qian Z, Fu LC. Joint development of cultural heritage protection and tourism: the case of Mount Lushan cultural landscape heritage site. Herit Sci. 2021;9(1):1–16.
Rongna A, Sun J. Integration and sustainability of tourism and traditional livelihood: a rhythm analysis. J Sustain Tour. 2020;28(3):455–74.
Zhang CZ, Fyall A, Zheng YF. Heritage and tourism conflict within world heritage sites in China: a longitudinal study. Curr Issue Tour. 2015;18(2):110–36.
Bloch N. Evicting heritage: spatial cleansing and cultural legacy at the Hampi UNESCO site in India. Crit Asian Stud. 2016;48(4):556–78.
Allen A, Lennon M. The values and vulnerabilities of ‘Star Wars Island’: exploring tensions in the sustainable management of the Skellig Michael world heritage site. Int J Sust Dev World. 2018;25(6):483–90.
Thinh NA, Thanh NN, Tuyen LT, Hens L. Tourism and beach erosion: valuing the damage of beach erosion for tourism in the Hoi An world heritage site, Vietnam. Environ Dev Sustain. 2019;21(5):2113–24.
Simsek S, Günay G, Elhatip H, Ekmekci M. Environmental protection of geothermal waters and travertines at Pamukkale, Turkey. Geothermics. 2000;29(4–5):557–72.
Galas A. Problems of the environmental resources management around Colca Canyon, Peru. Gospodarka Surowcami Mineralnymi-Miner Resour Manag. 2008;24(2):135–52.
Van Dijk J, Broersma L, Mehnen N. Options for socioeconomic developments in ICZM for the tri-national Wadden area. Ocean Coast Manag. 2016;119:76–92.
Heslinga J, Groote P, Vanclay F. Understanding the historical institutional context by using content analysis of local policy and planning documents: assessing the interactions between tourism and landscape on the Island of Terschelling in the Wadden Sea Region. Tour Manag. 2018;66:180–90.
Varghese J, Crawford SS. A cultural framework for Indigenous, local, and science knowledge systems in ecology and natural resource management. Ecol Monogr. 2021;91(1): e01431.
Yang R, Duan ZW, Du MJ, Miao X. A comprehensive knowledge pedigree on environmental transparency. Pol J Environ Stud. 2020;30(1):535–54.
Donthu N, Kumar S, Mukherjee D, Pandey N, Lim WM. How to conduct a bibliometric analysis: an overview and guidelines. J Bus Res. 2021;133:285–96.
Bhowmik P. Heritage tourism: a bibliometric review. Anatolia. 2021. https://doi.org/10.1080/13032917.2021.1875250.
Kumar S, Sureka R, Vashishtha A. The journal of heritage tourism: a bibliometric overview since its inception. J Herit Tour. 2020;15(4):365–80.
Chen CM. Science mapping: a systematic review of the literature. J Data Inf Sci. 2017. https://doi.org/10.1515/jdis-2017-0006.
Powell TH, Kouropalatis Y, Morgan RE, Karhu P. Mapping knowledge and innovation research themes: using bibliometrics for classification, evolution, proliferation and determinism. Int J Entrep Innov Manag. 2016;20(3–4):174–99.
Feng Y, Cui SZ. A review of emergency response in disasters: present and future perspectives. Nat Hazards. 2021;105(1):1109–38.
Xie L, Wang JW, Lv JH. Knowledge mapping of international dark tourism research: a bibliometric analysis using CiteSpace. Resour Sci. 2019;41(3):454–66 (In Chinese).
Marinello S, Butturi MA, Gamberini R, Martini U. Indicators for sustainable touristic destinations: a critical review. J Environ Plan Manag. 2021. https://doi.org/10.1080/09640568.2021.1978407.
Orgaz-Agüera F, Castellanos-Verdugo M, AcostaGuzmán JA, Cobeña M, Oviedo-García MDLÁ. The mediating effects of community support for sustainable tourism, community attachment, involvement, and environmental attitudes. J Hosp Tour Res. 2020;12:1–24.
Rastegar R, Zarezadeh Z, Gretzel U. World heritage and social justice: insights from the inscription of Yazd, Iran. J Sustain Tour. 2021;29(2–3):521–40.
Zheng DN, Liang ZX, Ritchie BW. Residents’ social dilemma in sustainable heritage tourism: the role of social emotion, efficacy beliefs and temporal concerns. J Sustain Tour. 2020;28(11):1782–804.
Kaltenborn BP, Thomassen J, Wold LC, Linnell JD, Skar B. World heritage status as a foundation for building local futures? A case study from Vega in Central Norway. J Sustain Tour. 2013;21(1):99–116.
Lee TH. Influence analysis of community resident support for sustainable tourism development. Tour Manag. 2013;34:37–46.
Tavares AO, Henriques MH, Domingos A, Bala A. Community involvement in geoconservation: a conceptual approach based on the geoheritage of South Angola. Sustainability. 2015;7(5):4893–918.
Eslami S, Khalifah Z, Mardani A, Streimikiene D, Han H. Community attachment, tourism impacts, quality of life and residents’ support for sustainable tourism development. J Travel Tour Mark. 2019;36(9):1061–79.
Wang N. Rethinking authenticity in tourism experience. Ann Tour Res. 1999;26(2):349–70.
Su XY, Sigley GG, Song CQ. Relational authenticity and reconstructed heritage space: a balance of heritage preservation, tourism, and urban renewal in Luoyang Silk Road Dingding Gate. Sustainability. 2020;12(14):5830.
Park E, Choi BK, Lee TJ. The role and dimensions of authenticity in heritage tourism. Tour Manag. 2019;74:99–109.
Fu X. Existential authenticity and destination loyalty: evidence from heritage tourists. J Destin Mark Manag. 2019;12:84–94.
Katahenggam N. Tourist perceptions and preferences of authenticity in heritage tourism: visual comparative study of George Town and Singapore. J Tour Cult Chang. 2020;18(4):371–85.
Latiff K, Ng SI, Aziz YA, Basha NK. Food authenticity as one of the stimuli to world heritage sites. Br Food J. 2019;122(6):1755–76.
Shen SY, Guo JY, Wu YY. Investigating the structural relationships among authenticity, loyalty, involvement, and attitude toward world cultural heritage sites: an empirical study of Nanjing Xiaoling Tomb, China. Asia Pac J Tour Res. 2014;19(1):103–21.
Kolar T, Zabkar V. A consumer-based model of authenticity: an oxymoron or the foundation of cultural heritage marketing? Tour Manag. 2010;31(5):652–64.
Wang Y. Customized authenticity begins at home. Ann Tour Res. 2007;34(3):789–804.
Lugosi P. Socio-technological authentication. Ann Tour Res. 2016;58:100–13.
Zhu YJ. Performing heritage: rethinking authenticity in tourism. Ann Tour Res. 2012;39(3):1495–513.
Reisinger Y, Steiner CJ. Reconceptualizing object authenticity. Ann Tour Res. 2006;33(1):65–86.
Aldighieri B, Testa B, Bertini A. 3D exploration of the San Lucano Valley: virtual geo-routes for everyone who would like to understand the landscape of the Dolomites. Geoheritage. 2016;8(1):77–90.
Orimoloye IR, Kalumba AM, Mazinyo SP, Nel W. Geospatial analysis of wetland dynamics: wetland depletion and biodiversity conservation of Isimangaliso Wetland, South Africa. J King Saud Univ Sci. 2020;32(1):90–6.
Liu J, Ren HG, Wang XY, Shirazi Z, Quan B. Measuring and predicting urban expansion in the Angkor region of Cambodia. Remote Sens. 2019;11(17):2064–85.
Koo S, Kim J, Kim C, Kim J, Cha HS. Development of an augmented reality tour guide for a cultural heritage site. J Comput Cult Herit. 2019;12(4):1–24.
Okura F, Kanbara M, Yokoya N. Mixed-reality world exploration using image-based rendering. J Comput Cult Herit. 2015;8(2):1–26.
Wright AM. Assessing the stability and sustainability of rock art sites: insight from southwestern Arizona. J Archaeol Method Theory. 2018;25(3):911–52.
Saintenoy T, Estefane FG, Jofré D, Masaguer M. Walking and stumbling on the paths of heritage-making for rural development in the Arica Highlands. Mt Res Dev. 2019;39(4):D1–10.
Wardell-Johnson G, Schoeman D, Schlacher T, Wardell-Johnson A, Weston M, Shimizu Y, et al. Re-framing values for a world heritage future: what type of icon will K’gari-Fraser Island become? Australas J Environ Manag. 2015;22(2):124–48.
Heslinga J, Groote P, Vanclay F. Towards resilient regions: policy recommendations for stimulating synergy between tourism and landscape. Land. 2020;9(2):44.
Li MM, Wu BH, Cai LP. Tourism development of world heritage sites in China: a geographic perspective. Tour Manag. 2008;29(2):308–19.
Berg F. Wear and tear of world heritage: preventive conservation and tourism in Norway’s stave churches. Stud Conserv. 2018;63(sup1):320–2.
Hardiman N, Burgin S. Effects of trampling on in-stream macroinvertebrate communities from canyoning activity in the Greater Blue Mountains world heritage area. Wetl Ecol Manag. 2011;19(1):61–71.
Lin MS, Xiao XN, Xu Y, Xie HB. The impact of water quality changes on tourism capacity at Golden Lake, China. J Food Agric Environ. 2013;11:1069–72.
Pan YD, Deng GP, Wang LZ, Cao Y, Pang WT, Wang QX, et al. Effects of in situ phosphorus enrichment on the benthos in a subalpine karst stream and implications for bioassessment in nature reserves. Ecol Ind. 2017;73:274–83.
Li QY, Wu JL, Zhou JC, Sakiev K, Hofmann D. Occurrence of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbon (PAH) in soils around two typical lakes in the western Tian Shan Mountains (Kyrgyzstan, Central Asia): local burden or global distillation? Ecol Indic. 2020;108: 105749.
Rasoolimanesh SM, Jaafar M, Kock N, Ramayah T. A revised framework of social exchange theory to investigate the factors influencing residents’ perceptions. Tour Manag Perspect. 2015;16:335–45.
Türker N. Host community perceptions of tourism impacts: a case study on the world heritage city of Safranbolu, Turkey. Revista de Cercetare şi Intervenţie Socială. 2013;43:115–41.
Tucker H, Boonabaana B. A critical analysis of tourism, gender and poverty reduction. J Sustain Tour. 2012;20(3):437–55.
Qian C, Sasaki N, Jourdain D, Kim SM, Shivakoti PG. Local livelihood under different governances of tourism development in China—a case study of Huangshan Mountain area. Tour Manag. 2017;61:221–33.
Chen FF, Xu HG, Lew AA. Livelihood resilience in tourism communities: the role of human agency. J Sustain Tour. 2020;28(4):606–24.
Jha S. Can natural world heritage sites promote development and social harmony? Biodivers Conserv. 2005;14(4):981–91.
Kim SS, Wong KK, Cho M. Assessing the economic value of a world heritage site and willingness-to-pay determinants: a case of Changdeok Palace. Tour Manag. 2007;28(1):317–22.
Okech RN. Socio-cultural impacts of tourism on world heritage sites: communities’ perspective of Lamu (Kenya) and Zanzibar Islands. Asia Pac J Tour Res. 2010;15(3):339–51.
Su DN, Nguyen NAN, Nguyen QNT, Tran TP. The link between travel motivation and satisfaction towards a heritage destination: the role of visitor engagement, visitor experience and heritage destination image. Tour Manag Perspect. 2020;34: 100634.
Hoang TDT, Brown G, Kim AKJ. Measuring resident place attachment in a world cultural heritage tourism context: the case of Hoi An (Vietnam). Curr Issue Tour. 2020;23(16):2059–75.
Shakoori A, Hosseini M. An examination of the effects of motivation on visitors’ loyalty: case study of the Golestan Palace, Tehran. Tour Manag Perspect. 2019;32: 100554.
Lee KY, Lee H. Traditional costume experience at a cultural heritage festival. Tour Manag Perspect. 2019;32: 100555.
Hew JJ, Leong LY, Tan GWH, Lee VH, Ooi KB. Mobile social tourism shopping: a dual-stage analysis of a multi-mediation model. Tour Manag. 2018;66:121–39.
Chen CF, Leask A, Phou S. Symbolic, experiential and functional consumptions of heritage tourism destinations: the case of Angkor world heritage site, Cambodia. Int J Tour Res. 2016;18(6):602–11.
Prayag G, Hosany S, Odeh K. The role of tourists’ emotional experiences and satisfaction in understanding behavioral intentions. J Destin Mark Manag. 2013;2(2):118–27.
Gannon M, Rasoolimanesh SM, Taheri B. Assessing the mediating role of residents’ perceptions toward tourism development. J Travel Res. 2021;60(1):149–71.
Escudero Gómez LA. Residents’ opinions and perceptions of tourism development in the historic City of Toledo, Spain. Sustainability. 2019;11(14):3854.
Md Noor S, Rasoolimanesh SM, Jaafar M, Barghi R. Inscription of a destination as a world heritage site and residents’ perceptions. Asia Pac J Tour Res. 2019;24(1):14–30.
Benham CF. Editor understanding local community attitudes toward industrial development in the Great Barrier Reef region world heritage area: are environmental impacts perceived to overshadow economic benefits? Natural Resources Forum; 2017: Wiley Online Library.
Della Lucia M, Franch M. The effects of local context on world heritage site management: the Dolomites natural world heritage site, Italy. J Sustain Tour. 2017;25(12):1756–75.
Aleshinloye KD, Fu X, Ribeiro MA, Woosnam KM, Tasci AD. The influence of place attachment on social distance: examining mediating effects of emotional solidarity and the moderating role of interaction. J Travel Res. 2020;59(5):828–49.
Yan HL, Bramwell B. Cultural tourism, ceremony and the state in China. Ann Tour Res. 2008;35(4):969–89.
Sun JX, Zhou Y, Wang XJ. Place construction in the context of world heritage tourism: the case of ‘Kaiping Diaolou and Villages.’ J Tour Cult Chang. 2019;17(2):115–31.
Othman J, Rahajeng A. Economic valuation of Jogjakarta’s tourism attributes: a contingent ranking analysis. Tour Econ. 2013;19(1):187–201.
Nicholas LN, Thapa B, Ko YJ. Residents’ perspectives of a world heritage site: the pitons management area, St. Lucia. Ann Tour Res. 2009;36(3):390–412.
Gao X, Roder G, Jiao YM, Ding YP, Liu ZL, Tarolli P. Farmers’ landslide risk perceptions and willingness for restoration and conservation of world heritage site of Honghe Hani Rice Terraces, China. Landslides. 2020;17(8):1915–24.
Wardana A. Neoliberalizing cultural landscapes: Bali’s agrarian heritage. Crit Asian Stud. 2020;52(2):270–85.
Martínez-Pérez Á, Beauchesne M-M. Overcoming the dark side of closed networks in cultural tourism clusters: the importance of diverse networks. Cornell Hosp Q. 2018;59(3):239–56.
Martínez-Pérez Á, Elche D, García-Villaverde PM, Parra-Requena G. Cultural tourism clusters: social capital, relations with institutions, and radical innovation. J Travel Res. 2019;58(5):793–807.
Chi CG, Zhang CZ, Liu YY. Determinants of corporate social responsibility (CSR) attitudes: perspective of travel and tourism managers at world heritage sites. Int J Contemp Hosp Manag. 2019. https://doi.org/10.1108/IJCHM-03-2018-0217.
Su LJ, Hsu MK, Swanson S. The effect of tourist relationship perception on destination loyalty at a world heritage site in China: the mediating role of overall destination satisfaction and trust. J Hosp Tour Res. 2017;41(2):180–210.
Weng LS, Liang ZX, Bao JG. The effect of tour interpretation on perceived heritage values: a comparison of tourists with and without tour guiding interpretation at a heritage destination. J Destin Market Manag. 2020;16: 100431.
Gao J, Zhang CZ, Liu L. Communicating the outstanding universal value of world heritage in China? The tour guides’ perspective. Asia Pac J Tour Res. 2020;25(9):1042–55.
Verma A, Rajendran G. The effect of historical nostalgia on tourists’ destination loyalty intention: an empirical study of the world cultural heritage site—Mahabalipuram, India. Asia Pac J Tour Res. 2017;22(9):977–90.
Alazaizeh MM, Ababneh A, Jamaliah MM. Preservation vs. use: understanding tourism stakeholders’ value perceptions toward Petra Archaeological Park. J Tour Cult Change. 2020;18(3):252–66.
Baral N, Kaul S, Heinen JT, Ale SB. Estimating the value of the world heritage site designation: a case study from Sagarmatha (Mount Everest) National Park, Nepal. J Sustain Tour. 2017;25(12):1776–91.
Dong XW, Zhang J, Zhi RZ, Zhong SE, Li M. Measuring recreational value of world heritage sites based on contingent valuation method: a case study of Jiuzhaigou. Chin Geogr Sci. 2011;21(1):119–28.
Parga-Dans E, González PA, Enríquez RO. The social value of heritage: balancing the promotion-preservation relationship in the Altamira world heritage site, Spain. J Destin Mark Manag. 2020;18: 100499.
Santos PM. Crossed gazes over an old city: photography and the ‘experientiation’ of a heritage place. Int J Herit Stud. 2016;22(2):131–44.
Wuepper D, Patry M. The world heritage list: which sites promote the brand? A big data spatial econometrics approach. J Cult Econ. 2017;41(1):1–21.
Veasna S, Wu WY, Huang CH. The impact of destination source credibility on destination satisfaction: the mediating effects of destination attachment and destination image. Tour Manag. 2013;36:511–26.
Brown S, Baldwin C, Chandler L. Representation of Butchulla cultural heritage values in communication of K’gari (Fraser Island) as a tourism destination. Australas J Environ Manag. 2015;22(2):163–80.
Yang CH, Lin HY. Revisiting the relationship between world heritage sites and tourism. Tour Econ. 2014;20(1):73–86.
Su YW, Lin HL. Analysis of international tourist arrivals worldwide: the role of world heritage sites. Tour Manag. 2014;40:46–58.
Gao YY, Su W. The disclosure of quality on tourism performance: evidence from top tourist cities in China. J Travel Res. 2021;60(7):1492–509.
Patuelli R, Mussoni M, Candela G. The effects of world heritage sites on domestic tourism: a spatial interaction model for Italy. J Geogr Syst. 2013;15(3):369–402.
Cellini R. Is UNESCO recognition effective in fostering tourism? A comment on Yang, Lin and Han. Tour Manag. 2011;32(2):452–4.
Santa-Cruz FG, López-Guzmán T. Culture, tourism and world heritage sites. Tour Manag Perspect. 2017;24:111–6.
Huang CH, Tsaur JR, Yang CH. Does world heritage list really induce more tourists? Evid Macau Tour Manag. 2012;33(6):1450–7.
Cuccia T, Guccio C, Rizzo I. The effects of UNESCO world heritage list inscription on tourism destinations performance in Italian regions. Econ Model. 2016;53:494–508.
Ribaudo G, Figini P. The puzzle of tourism demand at destinations hosting UNESCO world heritage sites: an analysis of tourism flows for Italy. J Travel Res. 2017;56(4):521–42.
Bak S, Min CK, Roh TS. Impacts of UNESCO-listed tangible and intangible heritages on tourism. J Travel Tour Mark. 2019;36(8):917–27.
Yang Y, Xue L, Jones TE. Tourism-enhancing effect of world heritage sites: Panacea or placebo? A meta-analysis. Ann Tour Res. 2019;75:29–41.
Yu GX, Dai GQ. Construction of Chinese and English event study knowledge system based on tourism perspective. Tour Tribune. 2018;2(33):90–104 (In Chinese).
Acknowledgements
The authors gratefully acknowledge the financial support of Guizhou normal university. We would also like to thank anonymous reviewers for their helpful and productive comments on the manuscript.
Funding
This work was supported by the Key Project of Science and Technology Program of Guizhou Province (No. 5411 2017 Qiankehe Pingtai Rencai), the World Top Discipline Program of Guizhou Province (No.125 2019 Qianjiao Keyan Fa), the China Overseas Expertise Introduction Program for Discipline Innovation (No.D17016), the Strategic Action Plan of Guizhou Undergraduate Higher Education Institutions to Serve the Rural Industrial Revolution(No. Qianjiaohe KY[2018]086), the Postgraduate Education Innovation Program Project of Guizhou Province (No. Qianjiaohe YJSCXJH [2020] 112).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
JZ and KNX developed the concept of this work. JZ wrote the manuscript, KNX and ZJL reviewed the whole text and made comments and suggestions to improve it. LXH edited parts of the manuscript. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Additional file 1: Appendix S1.
List of the 567 publications considered in bibliometric analysis.
Rights and permissions
Open Access This article is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License, which permits use, sharing, adaptation, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons licence, and indicate if changes were made. The images or other third party material in this article are included in the article's Creative Commons licence, unless indicated otherwise in a credit line to the material. If material is not included in the article's Creative Commons licence and your intended use is not permitted by statutory regulation or exceeds the permitted use, you will need to obtain permission directly from the copyright holder. To view a copy of this licence, visit http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/. The Creative Commons Public Domain Dedication waiver (http://creativecommons.org/publicdomain/zero/1.0/) applies to the data made available in this article, unless otherwise stated in a credit line to the data.
About this article
Cite this article
Zhang, J., Xiong, K., Liu, Z. et al. Research progress and knowledge system of world heritage tourism: a bibliometric analysis. Herit Sci 10, 42 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1186/s40494-022-00654-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1186/s40494-022-00654-0